Taxes in Georgia (country)
Discover the business-friendly environment of Georgia (country) renowned for its seamless startup process and attractive tax system. In 2020, Georgia secured the 7th spot on the global ease of doing business index, cementing its reputation as an entrepreneurial hub.
Setting up a and launching your business in Georgia can be accomplished within days, making it a top choice for investors. However, it’s not just the ease of doing business that attracts attention. Georgia boasts one of the lowest tax rates in Europe, making it an exotic destination for businesses.
Taxes in Georgia (country)? Ready to find out more
Simplified Tax Administration and Automated Services Streamlined tax administration is a standout feature in Georgia.
The majority of tax-related services are automated, ensuring a straightforward process for taxpayers. Each individual and business in Georgia receives a dedicated account on the official web portal of the Revenue Service of Georgia. This user-friendly platform enables taxpayers to conveniently file tax returns, generate tax invoices, submit applications, file appeals, and more.
A Comprehensive Overview of Taxes in Georgia. The tax system in Georgia is designed to be simple and cost-effective, with just six taxes to consider. Here’s a concise overview:
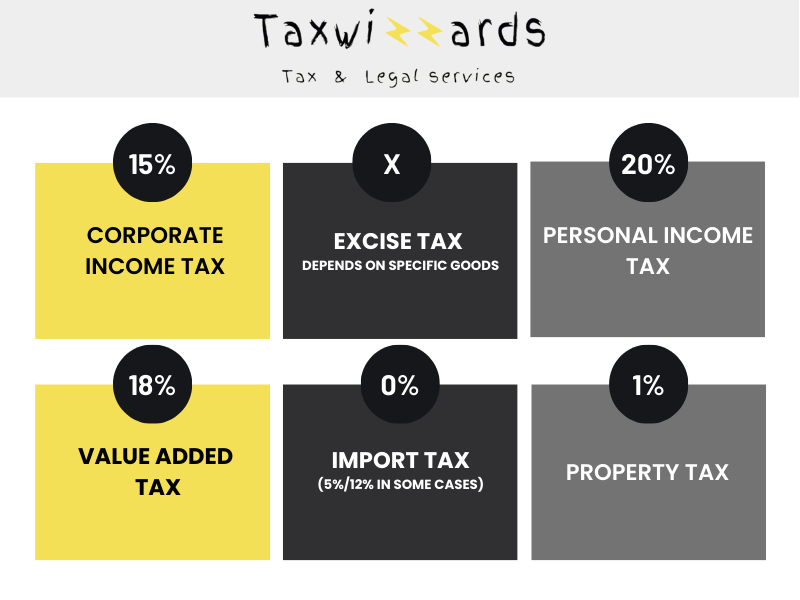
Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
Tax base: Georgian resident companies are not required to pay CIT, until the profit is distributed to the partner, that is a natural person or a non-resident entity. In such case, tax base is the amount of the distributed profit. Tax rate: 15%, Filing/payment deadline: Monthly – 15th day of the following month.
Dividend
Tax base: Georgian resident companies are not required to pay Dividend, until the profit is distributed to the partner, that is a natural person or a non-resident entity. In such case, tax base is the amount of the distributed profit. Tax rate: 5%, Filing/payment deadline: Monthly – 15th day of the following month.
Personal Income Tax (PIT)
Tax base: PIT taxable object is the difference between the gross income during the calendar year less respective deductions. Generally, all expenses related to earning income can be deducted from gross income, other than not deductible expenses specifically listed in the Tax Code of Georgia. Salary income is also subject to PIT without deductions. Though, salary is withheld at the source of payment by the employer. Tax rate: 20%. Filing/payment deadline: Yearly – 1st of April of the following year.
For more information about individual entrepreneurs see the article.
Value Added Tax (VAT)
Tax base: VAT taxable transaction is a supply of goods/services in the territory of Georgia. VAT tax base is the compensation in return for the supply of goods/services. VAT payers can credit input VAT and reduce the amount payable to the State Tax rate: 18%, Filing/payment deadline: Monthly – 15th day of the following month
Import Tax
Tax base: Taxable base for Import Tax is the customs value of the imported goods. The customs value is determined by the importer and checked by the customs authorities. Tax rate: 0%/5%/12%, Filing/payment deadline: 5 days after importing the goods
There is a defined list of products subject to tax rates of either 5% or 12%. (see: the first part of Article 197: where the list of which products are taxed at a rate of 12% and also at the same of the second part of the article: where there is a list of products that are taxed at a rate of 5%)
Excise Tax
Tax base: Excise Tax is levied on specific goods. These goods mainly include tobacco products, gas and oil products, alcohol, and motor vehicles. Tax base depends on the specific goods. Tax rate: Depends on the specific goods Filing/payment deadline: Monthly – 15th day of the following month.
Property Tax
Tax base: Property tax is imposed on the annual average net book value of fixed assets and/or investment property located in Georgia. Tax rate: Up to 1% Filing/payment deadline: Yearly – 1st of April of the following year
Social Security Tax and Mandatory Funded Pensions:
Georgia does not impose a social security tax. However, both employers and employees are required to contribute 2% of the gross salary to the Mandatory Funded Pensions. Employers are responsible for withholding the employee’s portion and making contributions on their behalf, resulting in dual contributions. (however, if your employee is non-Georgian you are free above mentioned pension tax)
Georgia (country) offers an enticing landscape for businesses, combining a favorable business environment with an appealing tax system. With simplified tax administration and automated services, managing taxes in Georgia becomes a hassle-free experience. The country’s low tax rates and straightforward compliance requirements make it an attractive option for businesses seeking financial stability and growth. By exploring the details of Georgia.

Tengo Tadumadze
CEO of the TaxwizzardsGeorgia
Aurthor of this article
Are you interested in more information?
Or maybe you have some additional questions?
contact us, consultation is FREE
Socials

